Concepts on Quiz 3
Before working through these practice questions, you should first carefully read this page on Quiz Expectations.
Quiz 3 will cover the following concepts:
- Lessons 18 through 21
Questions
The quiz itself will be similar in difficulty but longer in length than this practice worksheet.
Solutions for each problem can be found at the bottom of this page.
Conceptual Questions
- To access a value in a dictionary, you use the format
dictionary_name{key}. (T/F) - Multiple keys can have the same value. (T/F)
- The values in a dictionary cannot be changed after the dictionary is constructed. (T/F)
- The
not inoperator can be used to check whether a specific key exists in a dictionary. (T/F) - For the purposes of this course, all values in a dictionary are of the same type. (T/F)
- Dictionaries can have lists or other dictionaries as their keys. (T/F)
- In a Jupyter Notebook, you may evaluate the cells in any order. (T/F)
- You should write comments in a Python cell to narrate your code in a Jupyter Notebook. (T/F)
- Cells will automatically print output below them if the final line of the code assigns a value to a variable. (T/F)
- Restarting the Jupyter notebook’s kernel erases all of its variables that were previously assigned by running cells. (T/F)
Memory Diagrams
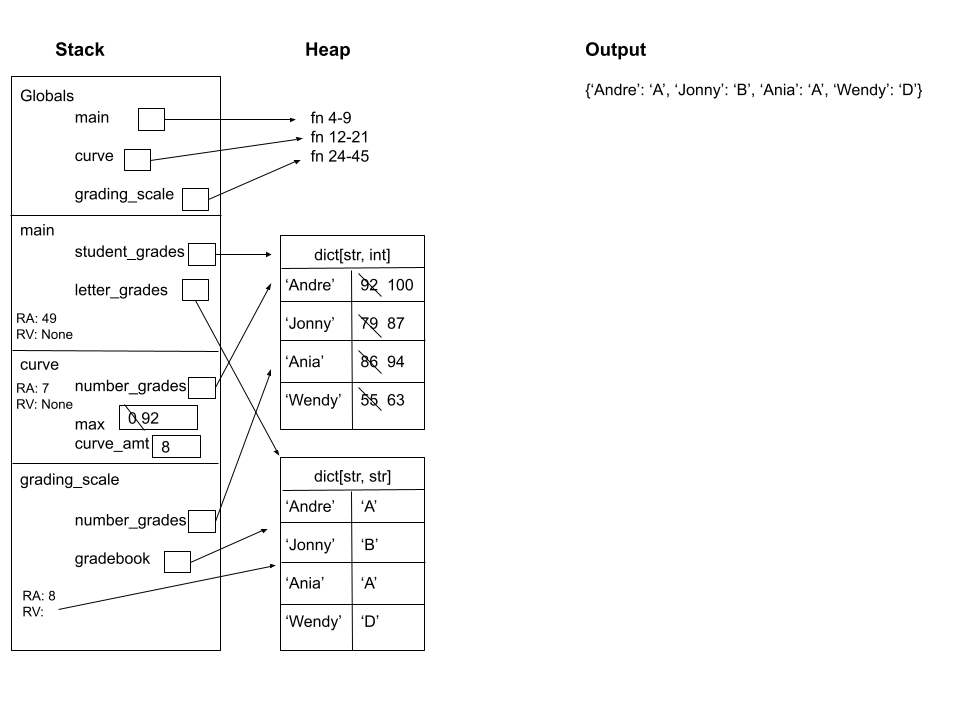
Produce a memory diagram for the following code snippet, being sure to include its stack and output.
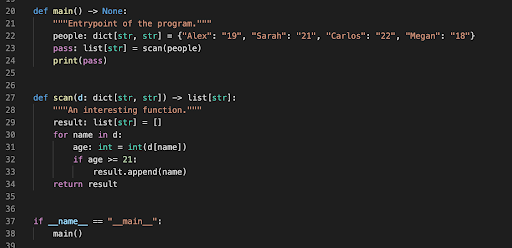
11.1 Describe in words what thescanfunction does.Produce a memory diagram for the following code snippet, being sure to include its stack and output.
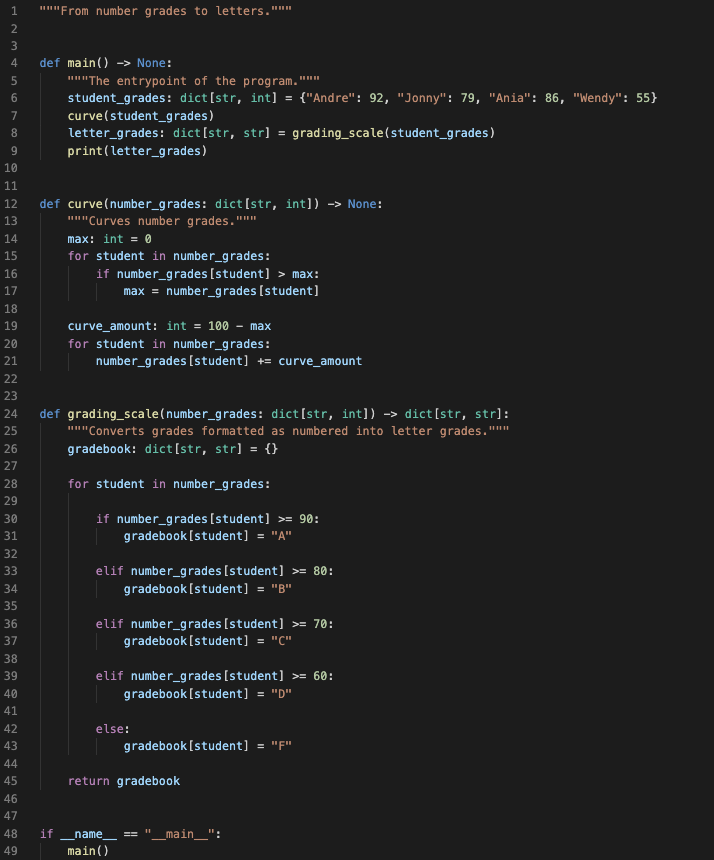
Function Writing
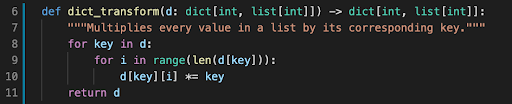
Write a function called
dict_transform. Given a dictionary withintkeys andlist[int]values,dict_transformshould return the dictionary with every value in a list multiplied by its corresponding key.
Example:dict_transform({ 2:[1,2] , 5:[3,4] })returns{ 2:[2,4] , 5:[15,20] }.Write a function called
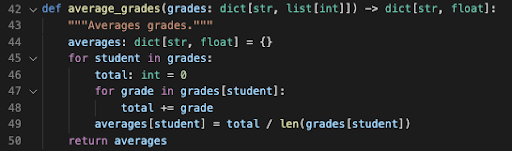
average_grades. Given a dictionary withstrkeys andlist[int]values,average_gradesshould return a new dictionary of typedict[str, float]that maps each student to their average.
Example:average_grades({ ‘Bill’:[75, 94, 97] , ‘Annie’:[88, 93, 99] })returns{ ‘Bill’:88.67 , ‘Annie’:93.33 }.
Solutions
Conceptual Questions
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- False
- True
Memory Diagrams

11.1 Thescanfunction takes in a dictionary and returns a list of the names of people that are 21 and older.